When applying for a mortgage, understanding your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio is essential. It’s one of the key factors lenders use to assess your ability to repay a loan. Your DTI ratio gives lenders insight into your financial health and helps determine how much you can afford in monthly mortgage payments. Here’s a detailed guide to understanding DTI ratios and how they affect your mortgage application.
What Is a Debt-to-Income Ratio?
A debt-to-income ratio is the percentage of your monthly income that goes toward paying debts. This ratio helps lenders gauge your financial stability and risk level. Simply put, it shows them how much of your income is already committed to existing obligations, such as credit card payments, car loans, and student loans.
How to Calculate Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
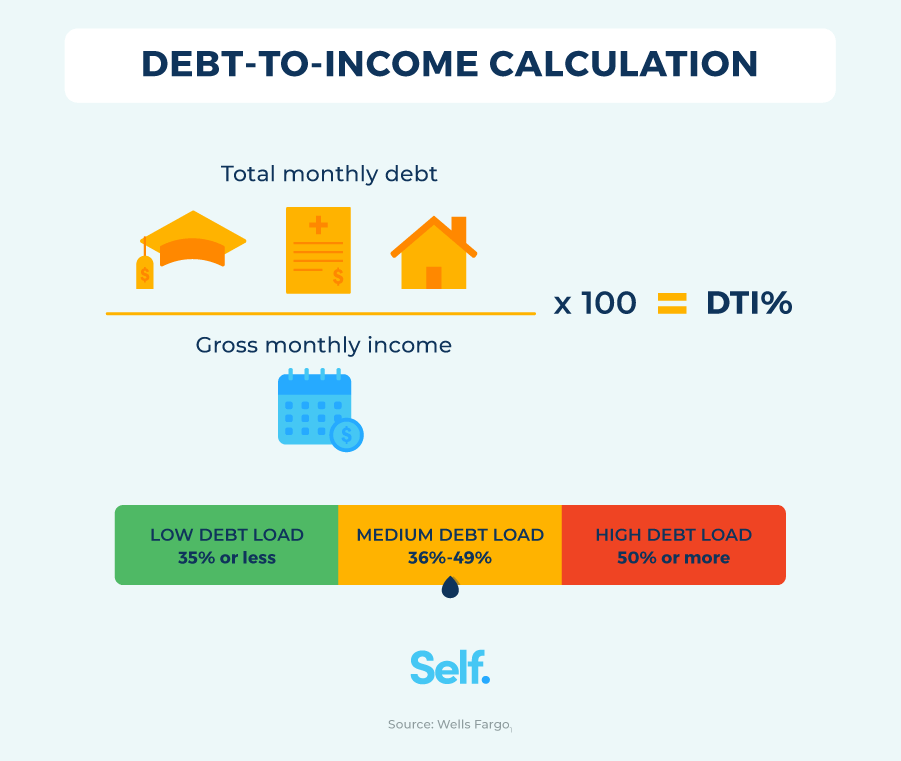
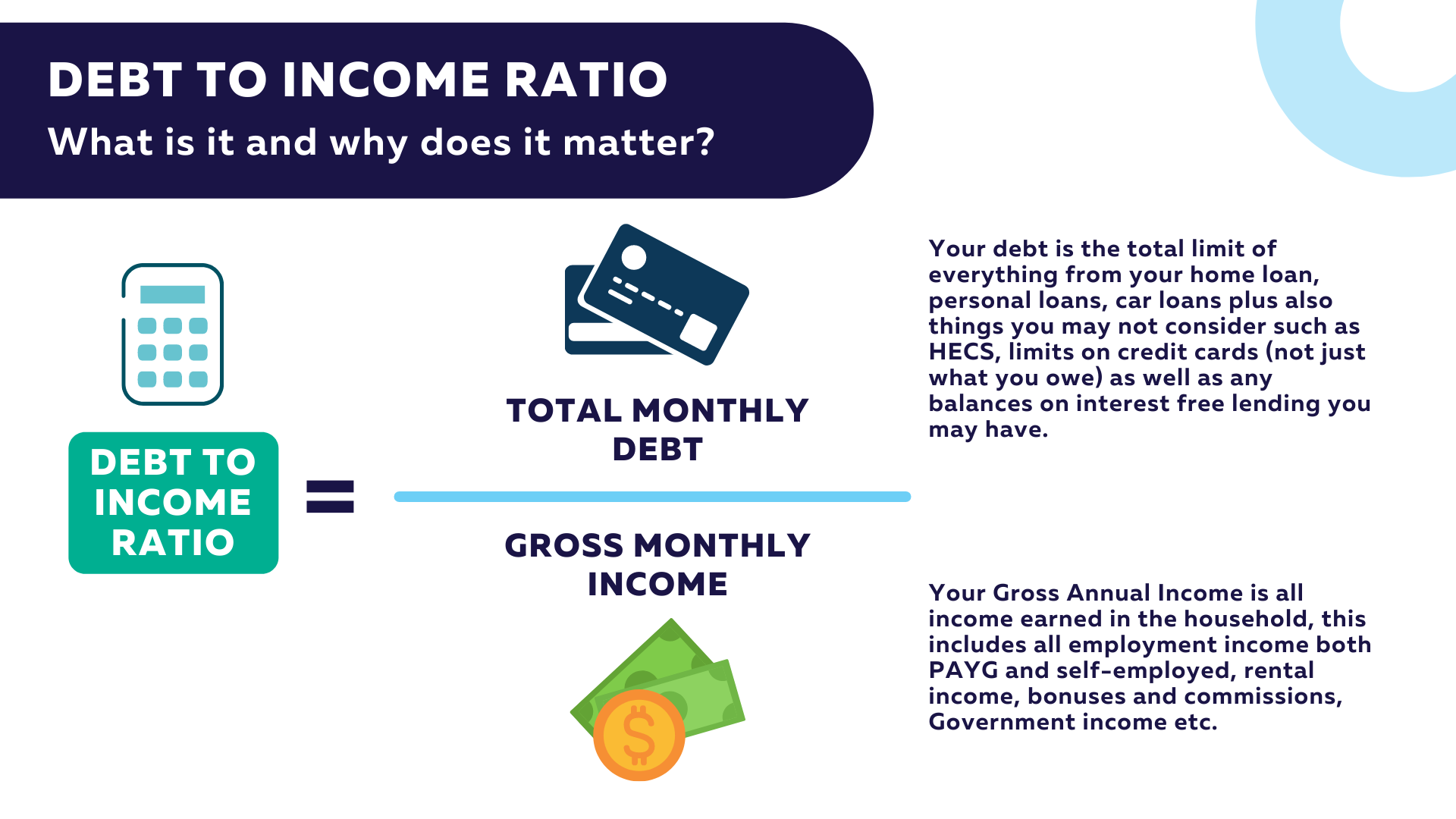
Calculating your DTI ratio is straightforward. Here’s the formula:
DTI Ratio = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) × 100
- Total Monthly Debt Payments: Add up all your monthly debt obligations, such as mortgage or rent payments, credit card bills, car loans, and personal loans.
- Gross Monthly Income: This is your income before taxes and deductions.
Example Calculation: Suppose your monthly debt payments are $1,500 and your gross monthly income is $5,000.
DTI Ratio = ($1,500 / $5,000) × 100 = 30%
This means that 30% of your monthly income goes toward debt payments.
Why Is Your DTI Ratio Important?
Lenders use your DTI ratio to evaluate your risk as a borrower. A lower DTI ratio indicates that you have a manageable level of debt relative to your income, making you a more attractive candidate for a mortgage. On the other hand, a high DTI ratio may signal to lenders that you have too many existing obligations, which could make it difficult for you to manage additional mortgage payments.

DTI Ratio Guidelines for Different Types of Loans
The acceptable DTI ratio varies based on the type of mortgage you’re applying for and the lender’s guidelines:
1. Conventional Loans: Most conventional loans require a DTI ratio of 43% or lower, but lenders may approve higher ratios if the borrower has a strong credit score, significant assets, or a large down payment.
2. FHA Loans: The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) is more flexible with DTI ratios. Typically, the maximum allowable DTI for FHA loans is 43%, though in some cases, borrowers with a strong credit profile may qualify with a DTI ratio up to 50%.
3. VA Loans: The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) does not set a strict DTI ratio requirement but recommends that borrowers aim for a DTI ratio of 41% or lower. However, lenders may approve higher ratios if the borrower has compensating factors like a high credit score or substantial savings.
4. USDA Loans: For loans backed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the recommended DTI ratio is generally up to 41%. The USDA, however, may make exceptions based on the borrower’s credit and financial situation.
What Is a Good DTI Ratio for a Mortgage?
A “good” DTI ratio can vary depending on the lender and the loan type. In general:
- Below 36%: Considered excellent. Borrowers with DTI ratios under 36% are seen as low-risk and are more likely to get better interest rates.
- 36% to 43%: Generally acceptable for most loan types. A DTI within this range shows that you can manage debt well, though it may not be optimal for the best mortgage terms.
- 43% to 50%: May still be approved, especially with certain loan types like FHA or VA loans. However, lenders may require compensating factors, such as a strong credit score or substantial down payment.
- Above 50%: Often considered risky. It may be difficult to get approved for a mortgage with a DTI above 50%, and if approved, you may face higher interest rates and stricter loan conditions.
How to Improve Your DTI Ratio
If your DTI ratio is higher than desired, there are steps you can take to improve it:
1. Pay Down Debt: Reduce outstanding balances on credit cards and loans to lower your monthly debt payments.
2. Increase Your Income: Boosting your income can decrease your DTI ratio. This could mean taking on additional work or finding ways to increase your current income.
3. Avoid Taking on New Debt: Refrain from opening new credit accounts or making large purchases that could increase your debt obligations.
4. Refinance Existing Debt: Refinancing high-interest debt into lower-interest loans can reduce your monthly payments and improve your DTI.
5. Make Larger Down Payments: For a mortgage, a larger down payment can reduce your monthly mortgage payment and lower your overall DTI.
How Your DTI Ratio Affects Mortgage Approval
Lenders use your DTI ratio, along with other factors like credit score, income, and savings, to determine if you qualify for a mortgage and what terms you’ll receive. A lower DTI ratio not only improves your chances of getting approved but can also help you secure a lower interest rate, potentially saving you thousands of dollars over the life of your loan.
Conclusion
Understanding your debt-to-income ratio is crucial in the home-buying process. By knowing your DTI and how it impacts your mortgage options, you can take proactive steps to improve your financial health. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or looking to upgrade your current living situation, being aware of your DTI ratio can set you up for mortgage success.

Hello welcome to my real estate service blog
